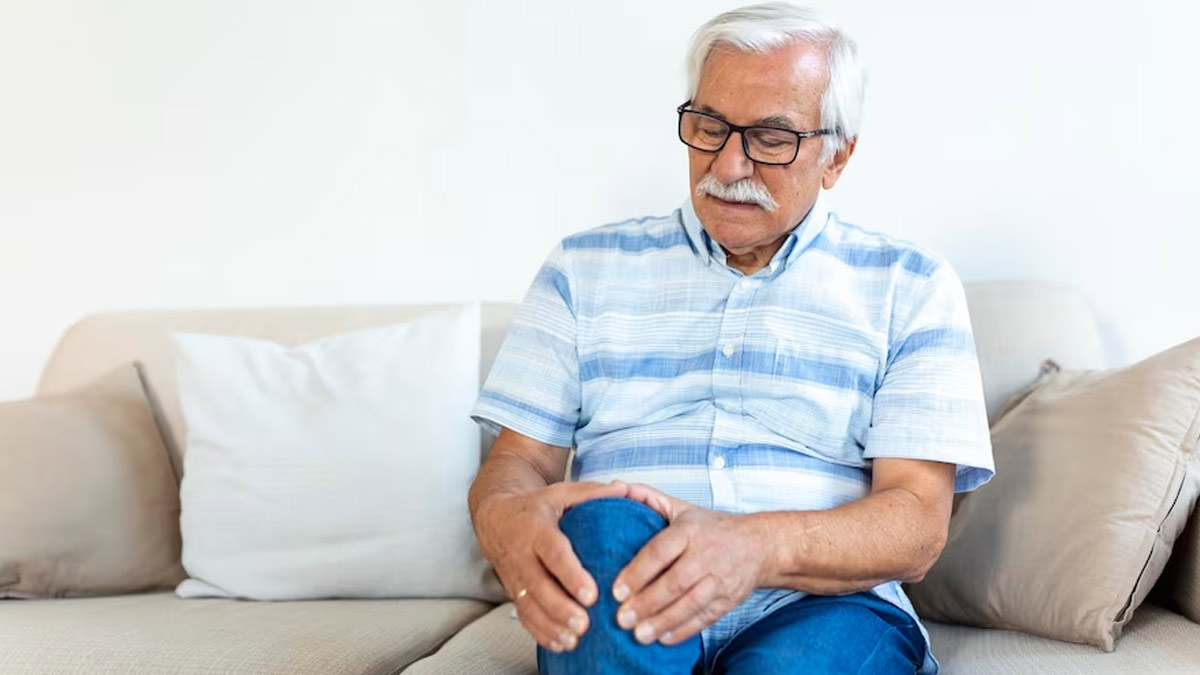
Gout is a common and extremely painful type of inflammatory arthritis that usually affects one joint at a time, according to the Centres For Disease Control And Prevention (CDC). Explaining why it’s essential to maintain gout, the medical watchdog and informant shared, ‘Having gout multiple times can lead to gouty arthritis, a form of arthritis which gets progressively worse.’ This must be taken seriously as ‘There is no cure for gout, but you can effectively treat and manage the condition with medication and self-management strategies.’
One essential self-management strategy that can help you manage gout is a healthy diet. So here is a breakdown of foods you should and should not eat if you suffer from gout.
Gout Diet Must Haves

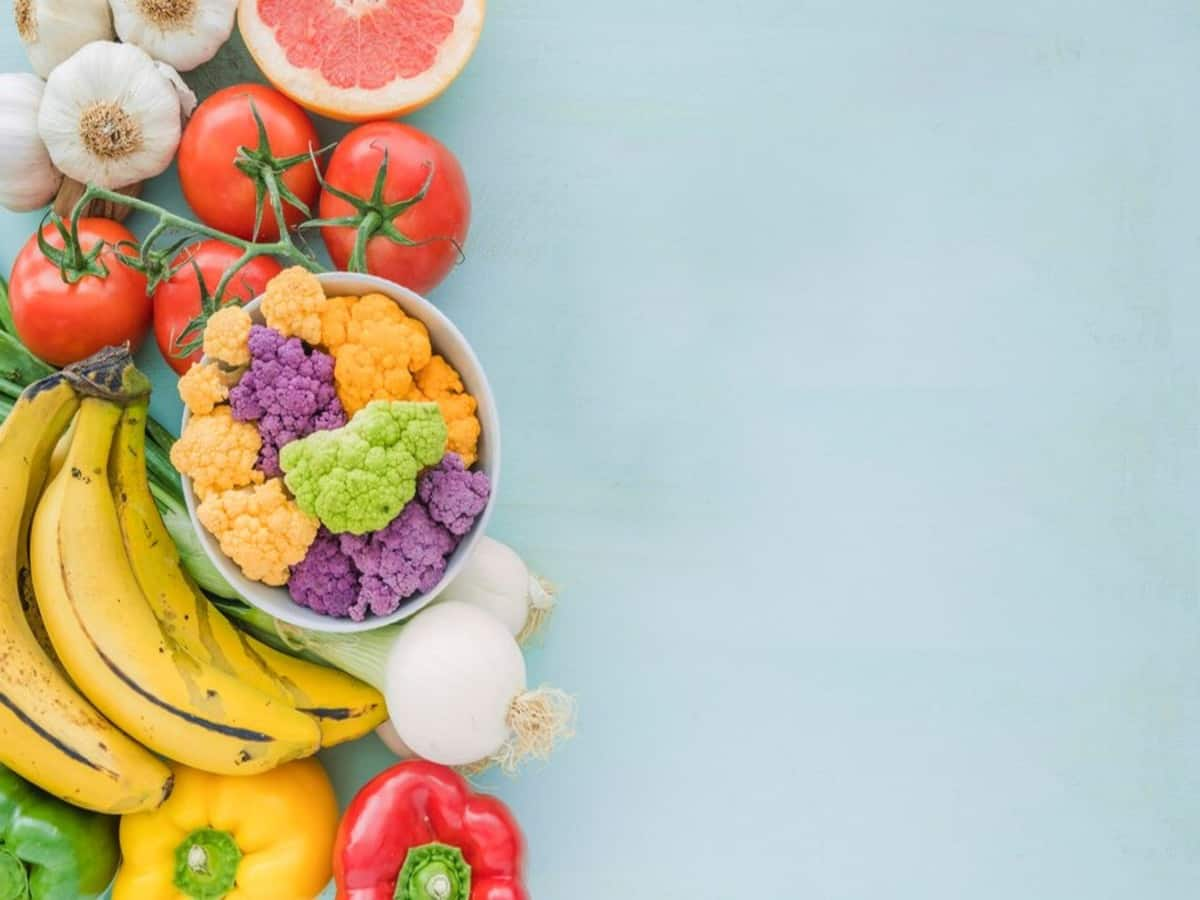
Gout can strike anyone, causing inflammation and extreme discomfort. A gout-friendly diet can help reduce the frequency and severity of gout attacks:
- Water: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out excess uric acid from your body.
- Low-Fat Dairy: Products like milk, yoghurt, and cheese can help reduce the risk of gout attacks.
- Fruits: Cherries, strawberries, and blueberries have been linked to lower levels of uric acid.
- Vegetables: Opt for a variety of vegetables, especially leafy greens, as they are rich in vitamins and nutrients.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Choose whole grains like brown rice, whole wheat, and oats over refined grains.
- Lean Proteins: Include lean sources of protein, such as chicken, turkey, and tofu, as they are less likely to trigger gout attacks.
Also Read: Gout: Expert Explains This Severe And Sudden Pain In The Joints
Foods To Avoid If You Have Gout
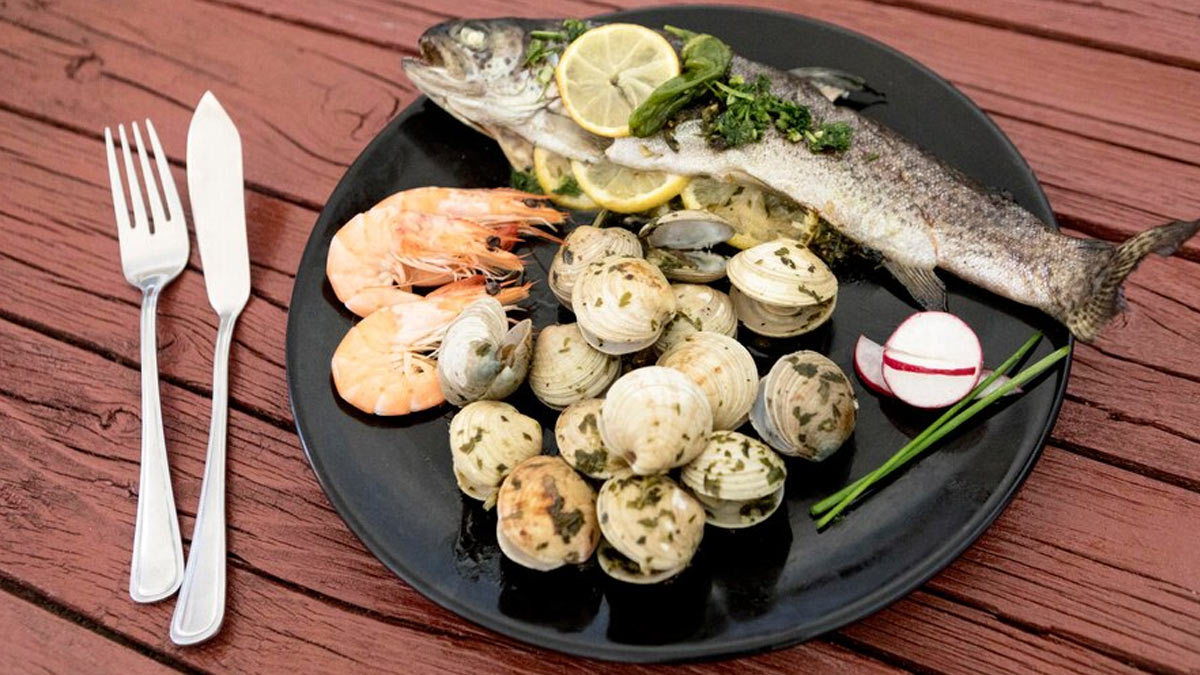

Gout is caused by excess buildup of uric acid in the joints, usually in the big toe. Uric acid is a waste product that usually gets flushed out through urine. However, for some people, the body produces too much uric acid or doesn’t eliminate it efficiently, leading to gout. Certain foods that can exacerbate the production of uric acid, or inflammation are:
- High-Purine Foods: Purines are compounds that break down into uric acid, and are usually found in red meat, organ meats, and seafood like shellfish.
- Alcohol: Alcohol, especially beer and spirits, can increase the risk of gout attacks.
- Sugary Beverages: High-fructose corn syrup, found in sugary drinks, has been associated with an increased risk of gout.
- Processed Foods: Processed foods are often high in sodium and unhealthy fats. They can contribute to gout attacks, so try to limit their consumption.
- Fatty Foods: Foods high in saturated and trans fats can lead to inflammation, which may trigger gout. Avoid fried foods and limit your intake of butter and margarine.
- Caffeine: Excessive caffeine intake may increase the risk of gout attacks.
Also Read: How To Treat Gout Naturally? Here Are 8 Useful Ways To Try at Home
Remember that dietary changes alone might not cure gout, but they can certainly help you manage and prevent painful episodes. Combining a gout-friendly diet with medication and lifestyle changes can help you take control of your gout and enjoy a better quality of life. Be patient, stay committed to a healthy diet, and consult with your healthcare provider for the best gout management plan for you.