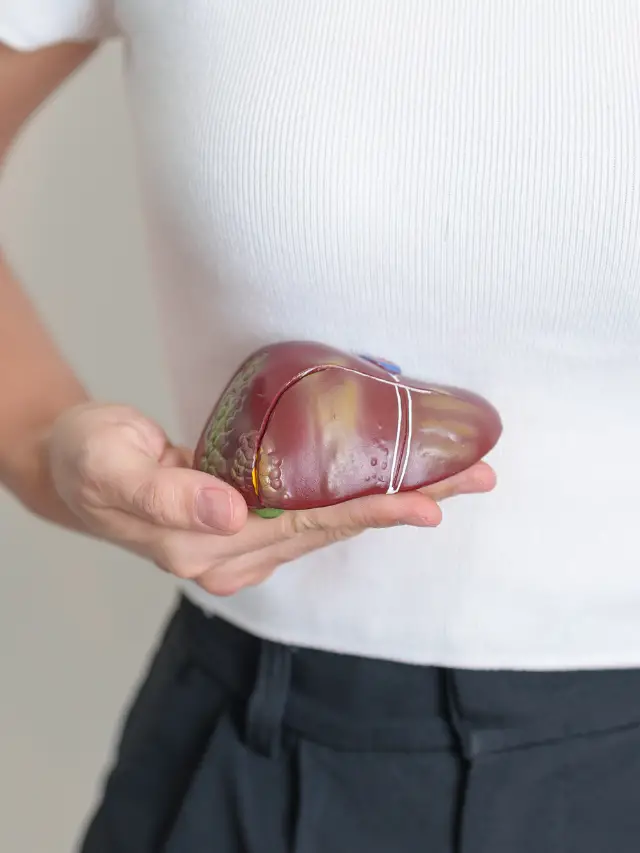
Fatty liver disease, medically termed hepatic steatosis, occurs when fat builds up in the liver cells, leading to potential complications. It’s a condition that often goes undetected in its early stages but can progress into more severe forms.
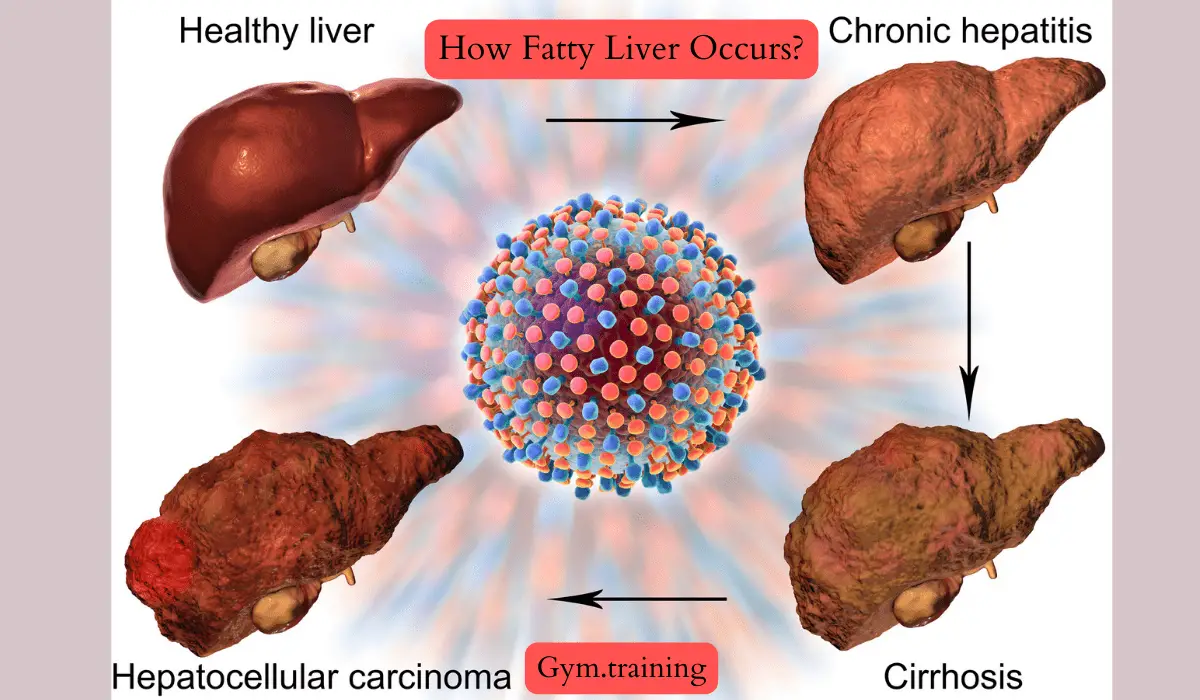
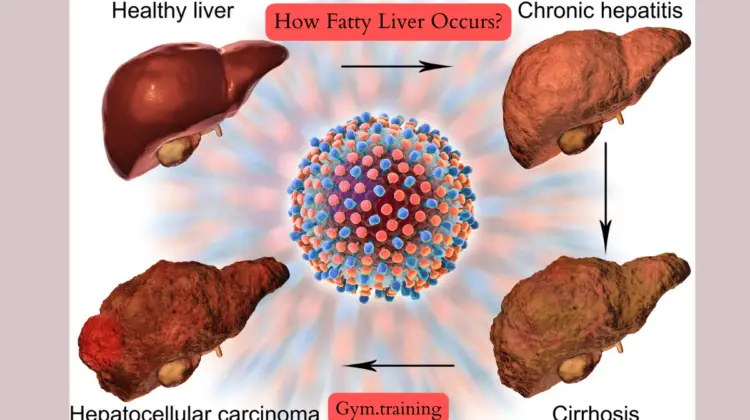
How Fatty Liver Occurs?
The condition referred to as fatty liver, or hepatic steatosis, is typified by the buildup of fat within the cells of the liver. Understanding how this occurs involves delving into its causes and mechanisms.
1. Dietary Factors
One primary cause of fatty liver is an excessive intake of fats and sugars. When the body receives more calories than it can burn, especially from foods high in saturated fats and refined sugars, the excess energy gets stored as fat in various organs, including the liver. The buildup causes the liver to become fatty.
2. Alcohol Consumption
Alcoholic liver disease is one consequence of alcohol abuse. The liver processes alcohol, and when the intake exceeds its processing capacity, it leads to the accumulation of fat in liver cells. This condition can progress to alcohol related liver diseases if alcohol consumption continues unabated.
3. Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome
Insulin resistance, often associated with obesity, plays a significant role in the development of fat liver. When the body becomes resistant to insulin, it leads to higher levels of insulin in the bloodstream, which triggers the liver to store more fat.
Metabolic syndrome, characterized by a combination of factors like high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels, also contributes to the development of fat liver. These conditions collectively promote fat accumulation in the liver.
4. Genetics and Medications
In some cases, genetic factors can predispose individuals to these liver disease. Certain genetic conditions affect how the body processes and stores fats, increasing the likelihood of fat accumulation in the liver.
Additionally, certain blood tests and medications, such as corticosteroids, tamoxifen, and some chemotherapy drugs, can cause or exacerbate liver by affecting how the liver metabolizes fats.
5. Other Contributing Factors
Other factors, like rapid weight loss, malnutrition, viral hepatitis, and certain infections, can also contribute to the development of fat liver by impacting the liver’s ability to process fats efficiently.
Fat liver occurs due to various factors, primarily stemming from eat a healthy diet to lifestyle choices, alcohol consumption, underlying health conditions, and genetic predispositions.
Understanding these causes through physical exam is crucial in adopting preventive measures and making lifestyle changes to manage and potentially reverse the condition.
Also Read: 10 Best Clean Eating Recipes For Sustainable Weight
Symptoms and Signs
- Early Indications: In the initial stages, individuals may not experience noticeable symptoms. However, fatigue, discomfort in the upper right abdomen, and mild jaundice can be early signs.
- Advanced Symptoms: As the condition progresses, symptoms may include abdominal swelling, enlarged liver, and in severe cases, complications like liver cirrhosis with other type of fatty liver diseases.
Treatment Options for Fatty Liver
This liver disease, characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, requires comprehensive management to prevent its progression and mitigate associated risk factors. The treatment approach involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and, in severe cases, medical interventions.
1. Lifestyle Modifications
- Dietary Changes: A fundamental aspect of treating this liver disease involves adopting a balanced diet. Emphasizing whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, while limiting saturated fats, refined sugars, and processed foods, helps in reducing fat buildup in the liver.
- Weight Management: It’s critical to limit calories and engage in regular exercise to reach and maintain a healthy weight. Your liver’s fat content can be greatly decreased and its function can be enhanced with even small weight loss.
- Limiting Alcohol: For individuals with alcoholic liver disease, abstaining from alcohol is vital to prevent further damage to the liver and allow for potential reversal of the condition.
2. Medications
- Insulin Sensitizers: Certain medications, like pioglitazone or metformin, commonly used for diabetes management, can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce fat accumulation in the liver.
- Vitamin E: Because of their antioxidant qualities, vitamin E supplements may occasionally be recommended to treat liver cell damage and inflammation.
- Other Medications: Physicians may recommend medications to manage associated conditions like high cholesterol or blood pressure, considering their impact on fat liver diseases.
3. Holistic Approaches
- Herbal Supplements: Some herbal supplements, such as milk thistle, may offer benefits in supporting liver health. However, their efficacy and safety should be discussed with a healthcare provider before use.
- Acupuncture and Mindfulness: Complementary therapies, such as mindfulness exercises or acupuncture, can help control stress levels, which can improve liver function and general health.
4. Medical Procedures
- Liver Transplant: In severe cases of liver disease where other treatments are ineffective, a liver transplantation might be considered. This is usually reserved for cases where the liver damage is extensive and life-threatening.
Also Read: 12 Natural Remedies For Boosting Immune System
Treatment for these fat liver problems involves a multi-faceted approach focusing on lifestyle modifications, medications, and sometimes medical procedures.
The goal is to reduce fat accumulation, alleviate symptoms, improve liver function, and prevent complications. To effectively manage this disease, seeking advice from healthcare specialists and following their instructions is essential.
Tips For Preventing Fatty Liver
- Fatty Liver and Diet: Keeping fat liver under control is made easier by eating a diet low in processed foods, sweets, and saturated fats and high in antioxidants and nutrients.
- Exercising with Fatty Liver: Walking, swimming, and cycling are examples of low-impact exercises that enhance general health and liver function.
- Medications for Fatty Liver: Physicians may prescribe medications like vitamin E or other medications to manage associated conditions.
- Managing Fatty Liver Holistically: Holistic approaches involving herbal supplements, acupuncture, and mindfulness practices complement traditional treatments in some cases.
- Fatty Liver in Children and Teens: Younger populations now have a higher prevalence of fat liver, which calls for early intervention measures and lifestyle changes.
- Support and Resources: Joining support groups and accessing reliable information sources can provide valuable insights and emotional support for individuals managing fat liver.
- Seeking Professional Help: Regular consultations with healthcare professionals, including hepatologists or gastroenterologists, aid in monitoring the condition’s progression and adjusting treatment plans.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is fatty liver reversible?
Fat liver can be reversible with lifestyle modifications in its early stages.
2. Can fatty liver lead to other health issues?
Yes, it can progress to liver inflammation, fibrosis, and potentially leads to liver failure or cancer.
3. What foods should be avoided with fatty liver?
Foods high in saturated fats, sugars, and processed foods should be limited.
4. Are there specific exercises beneficial for fatty liver?
Low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, and cycling are beneficial.
5. How often should one undergo check-ups for fatty liver?
Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are recommended for monitoring and managing the condition.